Pipeline Cables
Pipelines are used to direct the flow of material to and from different components. The pipelines are static which can be collided with but are themselves not affected by the collision.
The radius and spline control points can be configured in the simulation.
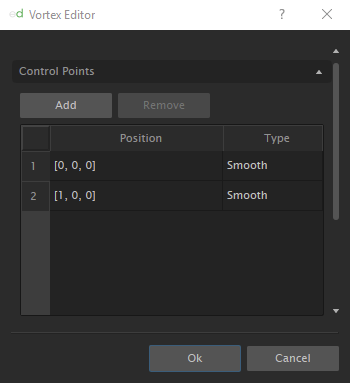
The shape of a pipeline is determined by control points. By default, a pipeline contains 2 control points. Control points can be added or removed by editing the Pipeline object. Control points can be moved and positioned using the editor move function or moved adjusting the origin and destination inputs.
Points will be distributed uniformly along the line of the pipeline and a collision geometry can be created between 2 consecutive points.
You can define a curvature at a given point by selecting a type:
- Smooth: The pipeline might not pass by the given control point but it is attracted by the point.
- Soft edge: The pipeline passes by the given control points and the first derivative is continuous.
- Hard: The pipeline pass by the given control points and but the first derivative is not continuous.
Creating Pipeline Cables
Using the cable system you can create long cables, or many cables specifically to pipeline simulation applications.
To add a pipeline cable system, complete the following.
In the Toolbox, select Cable Systems.
Select Pipeline and drag it into the 3D View, or into the desired mechanism in the Explorer panel.
Editing the Pipeline
In the Explorer panel, right-click the pipeline, and click Edit. From here, you can add, remove or edit control points. By default, two control points are created.
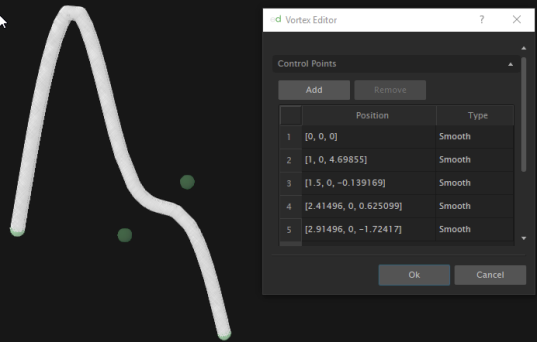
You can manually change the [x,y,z] position of a control point by selecting a point in the window or by moving the manipulator in the 3D view. Control points are represented by the green spots on the pipeline in the 3D View.
From the edit window, you can also change the type of curve the pipeline will have at the control points.
The choices are:
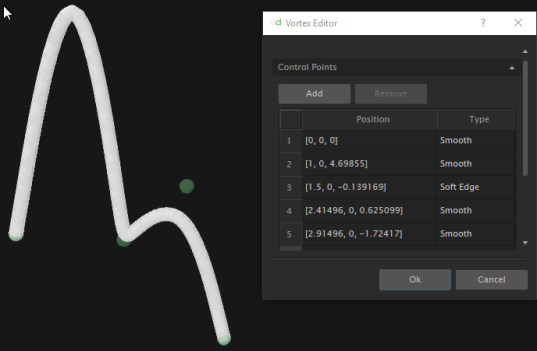
- Smooth: The pipeline might not pass by the given control point but it is attracted by the point.
- Soft Edge: The pipeline passes by the given control points and the first derivative is continuous.
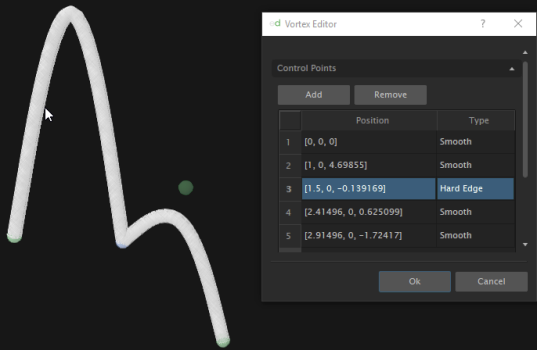
- Hard Edge: The pipeline passes by the given control points but the first derivative is not continuous.